JBC: A sugar-attaching enzyme defines colon cancer
Researchers have identified an enzyme that is absent in healthy colon tissue but abundant in colon cancer cells, according to published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
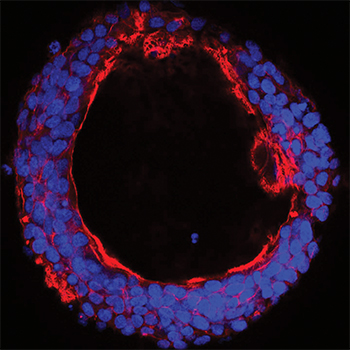 The enzyme GalNAc-T6 is upregulated selectively in colon adenocarcinomas, and its expression is associated with a cancerlike growth pattern.courtesy of Kirstine Lavrsen/University of Copenhagen
The enzyme GalNAc-T6 is upregulated selectively in colon adenocarcinomas, and its expression is associated with a cancerlike growth pattern.courtesy of Kirstine Lavrsen/University of Copenhagen
The enzyme appears to drive the conversion of normal colon tissue into cancer by attaching sugar molecules, or glycans, to certain proteins in the cell. Understanding the role that sugar-modified proteins play in healthy and cancerous cells is an emerging area of cancer biology that may lead to new therapies.
team at the studied 20 enzymes that initiate the first step in a particular kind of glycan modification, called GalNAc-type O-glycosylation, found on diverse proteins. These enzymes, called GalNAc transferases, or GalNAc-Ts, are found in different amounts in different tissues, but their functions are poorly understood.
Wandall’s team, led by then-graduate student , found that one of the GalNAc-Ts, called GalNAc-T6, was absent in healthy colon tissue but abundant in colon cancer cells. The team used CRISPR/Cas engineering of a colon cancer cell line with and without GalNAc-T6 to understand to which proteins the enzyme helped attach sugars and what effect this had on the cells.
“When we look at the 3D growth of a cancer cell line that has GalNAc-T6, it can form tubular structures with formation of something that looks like colon cancer tissue,” Wandall said. “When we take out GalNAc-T6, then suddenly the tissue formation changes to look more like the crypt structures that you would find in a healthy colon.”
Using mass spectrometry, the team categorized the proteins that GalNAc-T6 acted on in these cells.
“Our data suggest (that) this specific enzyme seems to affect a subset of proteins that could be involved in cell-cell adhesion,” Wandall said. In other words, the glycan modifications changed the patterns in which cells stuck together, leading the cells to develop as something that looked more like a tumor than a healthy tissue.
The next step is to understand precisely why adding sugars to the specific protein sites modified by GalNAc-T6 leads colon cells to develop abnormally. Glycan modifications can affect protein function in myriad ways. For example, they can make proteins that usually are cleaved into two unable to be cleaved, or prevent two proteins from binding to each other.
Wandall hopes that understanding glycosylation in cancer cells will lead to better early diagnostic tools, drugs or immunotherapies.
“Glycans add an additional context layer that could help us create more specific interventions,” he said.
“Glycans look so different in cancer compared to normal tissue, and it’s a really understudied field,” Lavrsen said. “There are a lot of things to be discovered.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Mapping fentanyl’s cellular footprint
Using a new imaging method, researchers at State University of New York at Buffalo traced fentanyl’s effects inside brain immune cells, revealing how the drug alters lipid droplets, pointing to new paths for addiction diagnostics.

Designing life’s building blocks with AI
Tanja Kortemme, a professor at the University of California, San Francisco, will discuss her research using computational biology to engineer proteins at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Cholesterol as a novel biomarker for Fragile X syndrome
Researchers in Quebec identified lower levels of a brain cholesterol metabolite, 24-hydroxycholesterol, in patients with fragile X syndrome, a finding that could provide a simple blood-based biomarker for understanding and managing the condition.

How lipid metabolism shapes sperm development
Researchers at Hokkaido University identify the enzyme behind a key lipid in sperm development. The findings reveal how seminolipids shape sperm formation and may inform future diagnostics and treatments for male infertility.

Mass spec method captures proteins in native membranes
Yale scientists developed a mass spec protocol that keeps proteins in their native environment, detects intact protein complexes and tracks drug binding, offering a clearer view of membrane biology.

Laser-assisted cryoEM method preserves protein structure
University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers devised a method that prevents protein compaction during cryoEM prep, restoring natural structure for mass spec studies. The approach could expand high-resolution imaging to more complex protein systems.

.jpg?lang=en-US&width=300&height=300&ext=.jpg)